

Get a grip on phonics by browsing our glossary of phonics terms.

Author
Lucy Hart
Updated
June 2024


Get a grip on phonics by browsing our glossary of phonics terms.

Author
Lucy Hart
Updated
June 2024


Get a grip on phonics by browsing our glossary of phonics terms.

Author
Lucy Hart
Updated
June 2024


Key takeaways
Table of contents
Phonics help children learn to read by teaching them to say the sounds that letters or groups of letters represent. It sounds simple, but it can be daunting when you’re faced with technical vocabulary like ‘split digraphs’, ‘phonemes’ and ‘graphemes’!
Below, we break down key phonics terms into a handy list of definitions to help you aid your child at home.
For simplicity, we have organised our list of phonics key terms in alphabetical order.
Blending involves merging the sounds in a word together in order to pronounce it. This is important for reading. For example, j-a-m blended together reads the word jam.
Two or three consonants next to each other that represent different sounds. For example, bl in black. Notice here that bl makes the two different sounds b and l, whereas ck makes the single sound ck.
Consonants are the letters of the alphabet (apart from the vowels a, e, i, o and u).
A digraph that is made up of two consonants (sh in shop).
An abbreviation for consonant-vowel-consonant. This is a simple way of indicating the order of the graphemes in words. For example, it (VC), cat (CVC), bench (CVCC).
A grapheme made up of two letters that makes one sound (sh in fish).
A grapheme is simply a way of writing down a phoneme. A grapheme can be one letter (s), two letters (ir), three letters (igh) or four letters in length (tough).
Unlock unlimited phonics practice!
Put your skills to the test with fun exercises + learning games that are proven to boost ability!
Learn phonics with DoodleEnglish! Filled with thousands of reading, grammar, spelling, and punctuation exercises aligned to the English national curriculum, 5 minutes of practice a day can improve reading and comprehension skills!
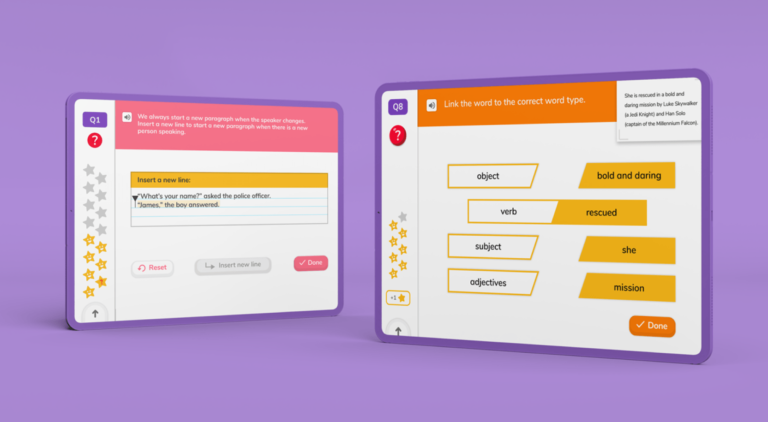
Knowing your GPCs means being able to hear a phoneme and knowing what grapheme to use to represent it. This is helpful for spelling. Conversely, it also means seeing a grapheme and knowing the phoneme that relates to it, which is important for reading.
The smallest unit of sound in a word. There are around 44 phonemes in English and they are represented by graphemes in writing. Phonemes are usually shown as symbols between two forward slashes. For example, /b/ or /ch/.
Segmenting involves breaking up a word that you hear into its sounds. This helps with spelling because if you know what graphemes represent the sounds in the word, you can write it! For example, the word jam is segmented into the sounds j-a-m.
A digraph that is split between a consonant (a-e in make). A split digraph usually changes the sound of the first vowel. For example, compare the pronunciation between hug and huge.
Words that are commonly used in English, but they have complex spelling patterns which make them difficult to read and write. For example: said, of and was.
A grapheme made up of three letters that makes one sound (igh in high).
Vowels are the letters a, e, i, o, and u in the alphabet.
A digraph that is made up of two vowels (ea in sea).
Learn all about phonics with DoodleEnglish, the personalised learning app for ages 7-11!
Filled with thousands of interactive exercises, games and collectables, DoodleEnglish guides children through the nation English curriculum, helping them to get back on track and top up their learning.
Book a chat with our team
If you’d like to use Doodle’s browser version, please visit this page on a desktop.
To log in to Doodle on this device, you can do so through our apps. You can find out how to download them here: