

Whether you’re a student or are looking to improve your numeracy skills, understanding rational numbers is crucial. Let’s discover what makes rational numbers so fascinating!

Author
Doodle Team
Published
December 5, 2023


Whether you’re a student or are looking to improve your skills, understanding rational numbers is crucial. Let’s discover what makes rational numbers so fascinating!

Author
Doodle Team
Published
Dec 5, 2023


Whether you’re a student or are looking to improve your numeracy skills, understanding rational numbers is crucial. Let’s discover what makes rational numbers so fascinating!

Author
Doodle Team
Published
Dec 5, 2023


Key takeaways
Table of contents
Are you ready to unlock the secrets of the number universe? Let’s dive deep into the world of rational numbers, where fractions and decimals unite to create a mathematical wonderland.
Rational numbers may seem daunting at first, but don’t let their complexity fool you – they’re the building blocks of many important mathematical concepts.
Whether you’re a student, a maths enthusiast or are simply looking to improve your numeracy skills, understanding rational numbers is crucial.
So, let’s embark on this mathematical adventure together and discover what makes rational numbers so fascinating!
Unlock unlimited maths questions
Put your learning into practice with fun exercises + games that are proven to boost ability!
Get 2 FREE weeks of Doodle!
Use code 2WKS_2026 to enjoy unlimited questions and games
Get 1 FREE month of Doodle!
Use code MONTH_2026 to enjoy unlimited questions and games
Have you ever asked yourself, ‘What is a rational number?’. If the answer is yes, you’re in luck!
A rational number is a number that can be expressed as a fraction of two integers, where the denominator is not zero.
In other words, it’s a number that can be written in the form of a/b, where a and b are integers and b is not equal to zero. Rational numbers can also be expressed as terminating or repeating decimals.
Rational numbers are numbers that can be expressed as a ratio of two integers. There are two main types of rational numbers: proper and improper fractions.
In addition to proper and improper fractions, there are also mixed numbers, which are a combination of a whole number and a proper fraction.
Try DoodleMaths for free!
Select a year group
A proper fraction is a rational number where the numerator is less than the denominator. Some examples of proper fractions include:
1/2
3/4
7/8
2/3
An improper fraction, on the other hand, is a rational number where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator.
Some examples of an improper fraction include:
5/2
3/2
7/4
2/1
Mixed numbers are a combination of a whole number and a proper fraction.
Some examples of mixed numbers include:
1 1/2
2 2/3
1 1/4
3 2/5
Adding and subtracting rational numbers is a fundamental skill in mathematics that can be easily mastered with a little practice. To add or subtract rational numbers, we need to follow a series of steps.
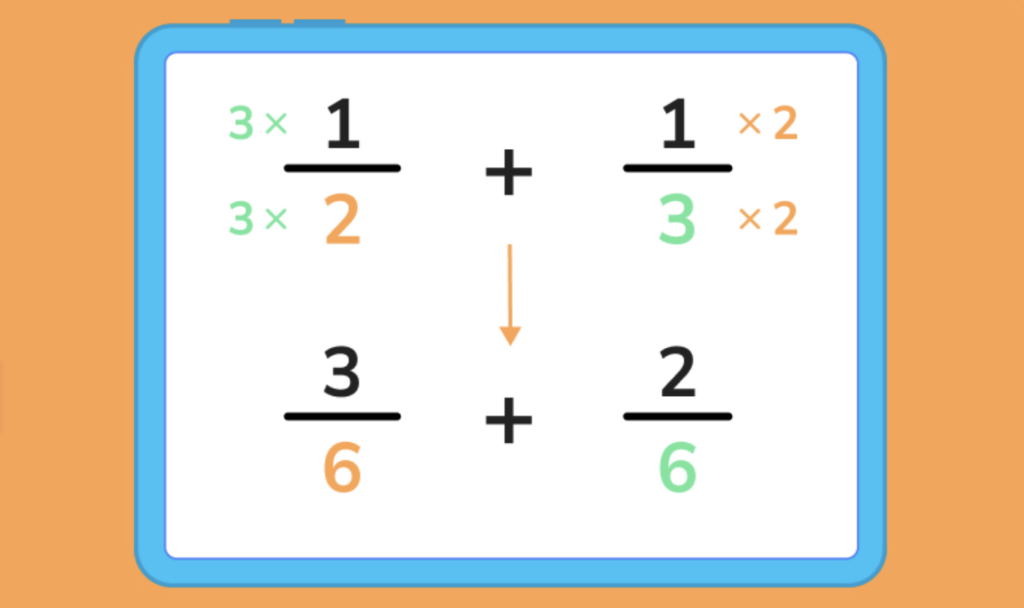
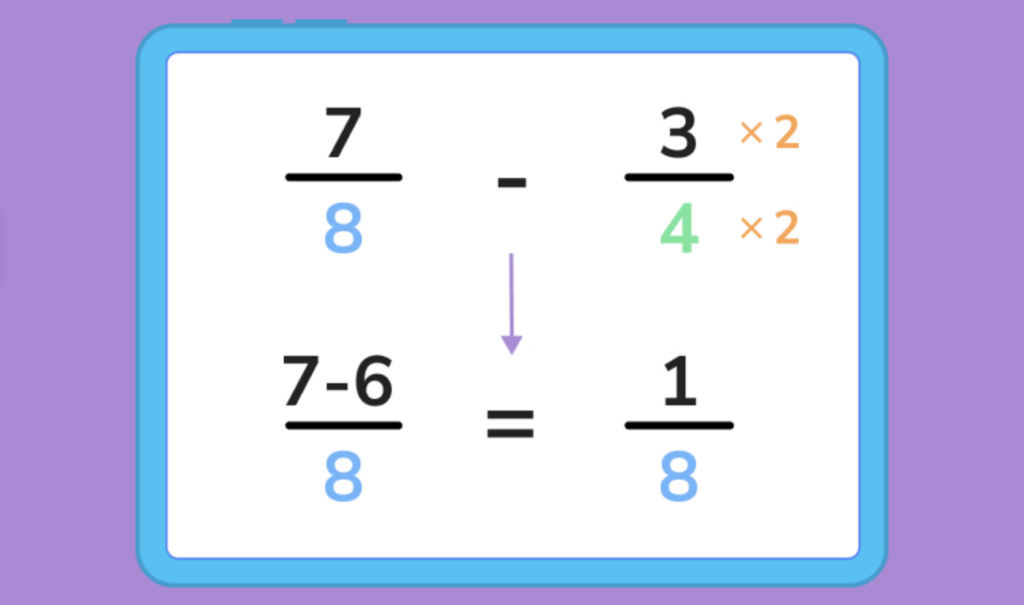
Step 1: Make sure that the fractions have the same denominator. To do this, we can find a common multiple of the denominators and convert each fraction into an equivalent fraction with that common denominator.
Step 2: Add or subtract the numerators and keep the common denominator.
To add:
To subtract:
Step 1: Multiply the numerators together.
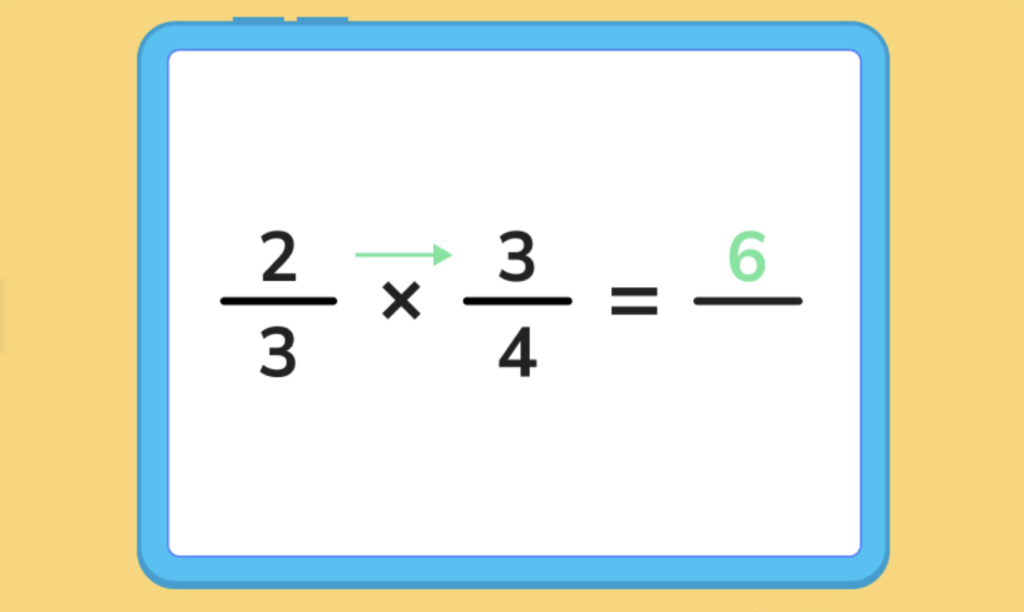
Step 2: multiply the denominators together.
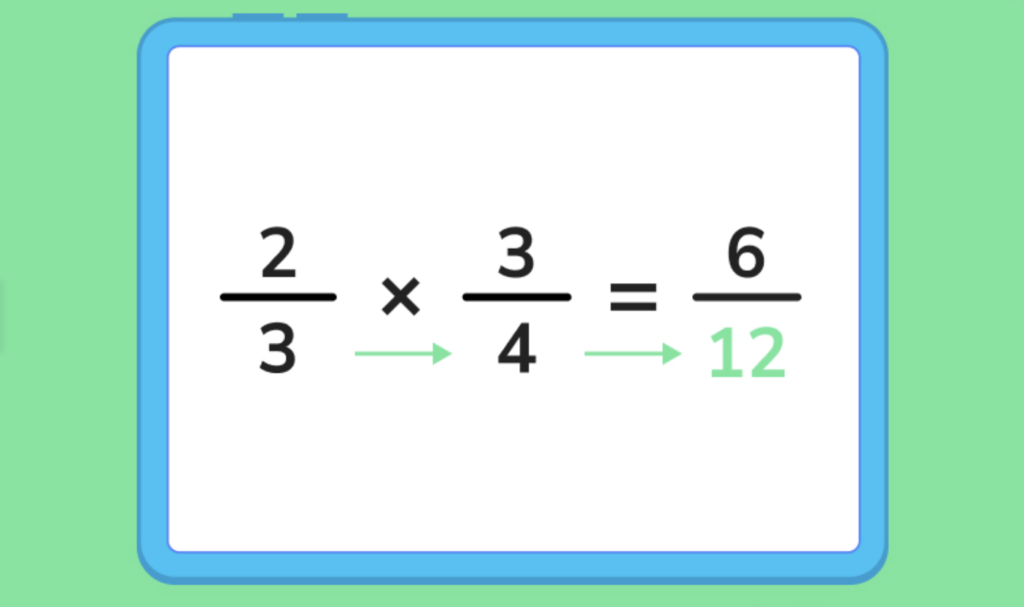
Step 3: simplify the fraction as needed. In this example, doing so gives us 1/2!
Step 1: Find the reciprocal of the second fraction by ‘flipping it’.
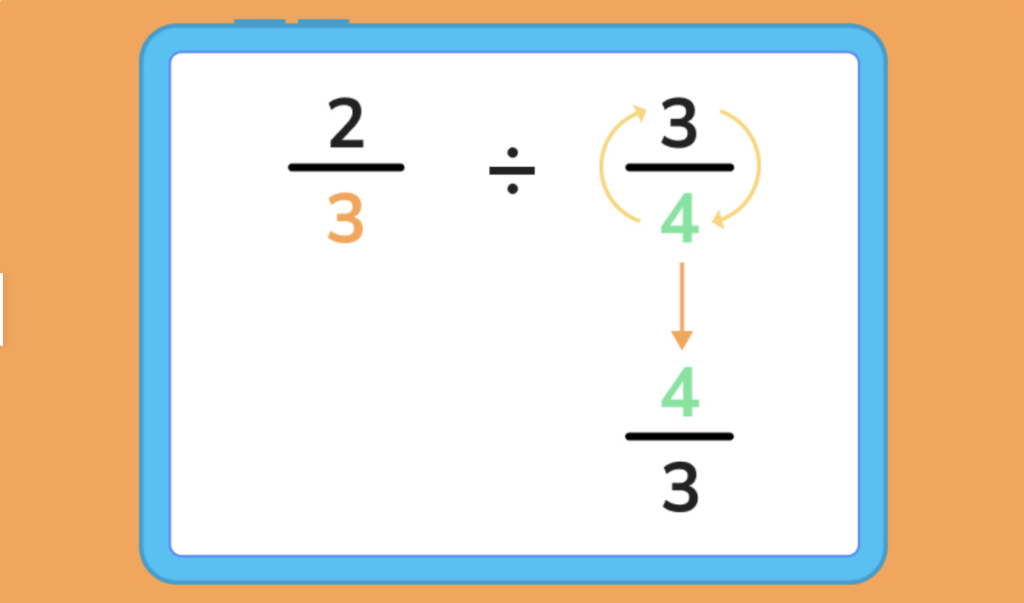
Step 2: multiply the numerators together.
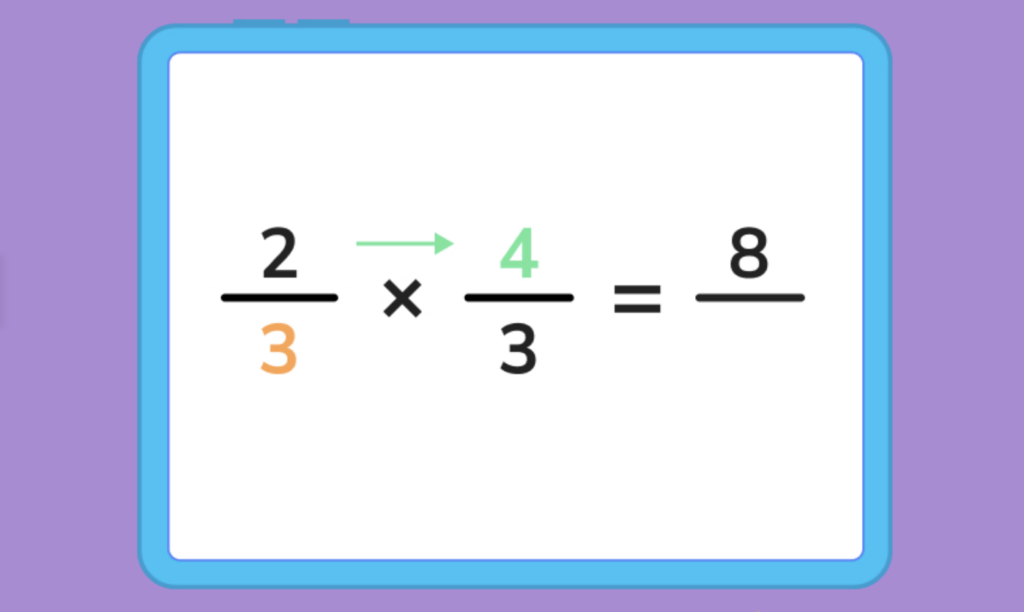
Step 3: Multiply the denominators together.
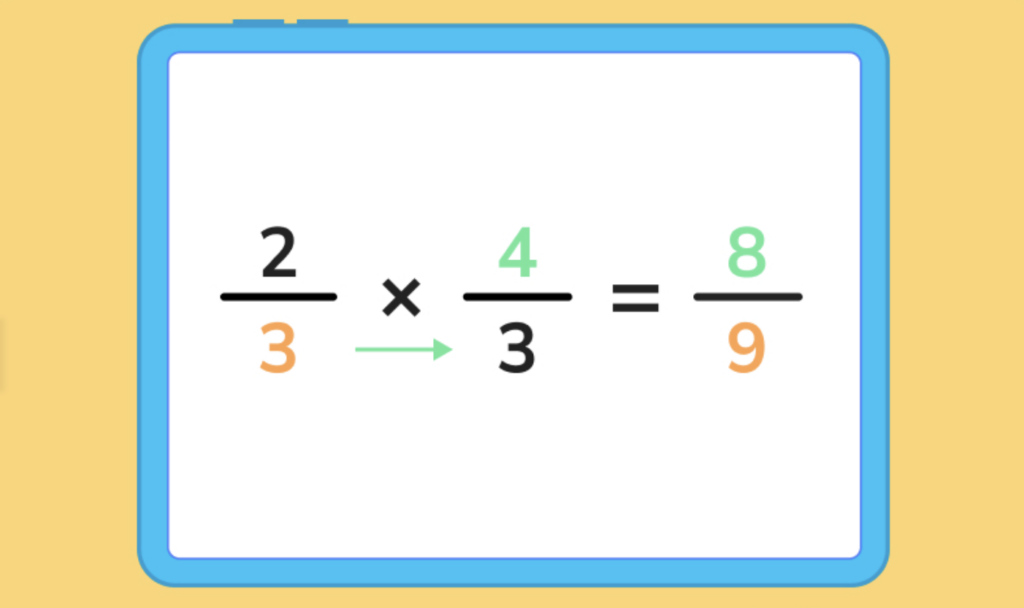
Step 4: Simplify the fraction as needed. In this example, we can’t simplify the fraction. This gives us a final fraction of 8/9 (or 8 over 9)!
Meet DoodleMaths, the award-wining maths app that’s proven to double a child’s rate of progression with just 10 minutes of use a day!*
Filled with fun, interactive questions covering the whole curriculum, it creates each child a unique work programme tailored to their needs, boosting their confidence and skills in the subject. Try it for free today!

*Based on earning 24 stars a day in DoodleMaths. Read full study
Yes, zero is a rational number. A rational number is any number that can be expressed as a ratio of two integers, and zero can be expressed as the ratio of 0 to any non-zero integer, such as 0/1, 0/2, 0/3, and so on.
Yes, fractions are rational numbers. A rational number is any number that can be expressed as the ratio of two integers, and a fraction is a type of number that is expressed as the ratio of two integers, where the denominator is not equal to zero. For example, 1/2, 5/8, and -3/4 are all examples of fractions that are also rational numbers.
Not all decimals are rational numbers, but some are.
A decimal is a number expressed in base 10, with a decimal point and digits that follow.
A decimal is rational if and only if it terminates (ends) or repeats a pattern. For example, the decimal 0.5 terminates, so it is a rational number that can be expressed as the fraction 1/2.
Likewise, the decimal 0.333… repeats the pattern “3” infinitely, so it is a rational number that can be expressed as the fraction 1/3.
However, the decimal 0.12345678910111213141516… goes on infinitely without repeating a pattern, and is therefore not a rational number.
Yes, rational numbers can be negative. A rational number is any number that can be expressed as the ratio of two integers, and this includes both positive and negative numbers. For example, 1/2, -3/4, and 5/6 are all examples of rational numbers, whereas -3/4 and 5/6 are negative rational numbers.
Yes, all integers are rational numbers. A rational number is any number that can be expressed as the ratio of two integers, and every integer can be expressed as the ratio of that integer and 1.
The main difference between rational and irrational numbers is that rational numbers can be expressed as a fraction, while irrational numbers cannot be expressed in this way.


Parents, sign up for a DoodleMaths subscription and see your child become a maths wizard!
Rational vs irrational numbers
Explore the differences between rational and irrational numbers
What is standard form?
Discover how standard form helps us represent numbers and equations clearly
Book a chat with our team
If you’d like to use Doodle’s browser version, please visit this page on a desktop.
To log in to Doodle on this device, you can do so through our apps. You can find out how to download them here: