

Area in maths: A measure of the space inside a shape. Learn the area formula for various shapes and real-world applications.

Author
Michelle Griczika
Published
January 2024


Area in maths: A measure of the space inside a shape. Learn the area formula for various shapes and real-world applications.

Author
Michelle Griczika
Published
January 2024


Area in maths: A measure of the space inside a shape. Learn the area formula for various shapes and real-world applications.

Author
Michelle Griczika
Published
January 2024


Key takeaways
Table of contents
The concept of area in maths is more than just numbers and shapes; it’s about real-life applications. Picture this – choosing the right amount of paint for a wall or a room’s carpet size. That’s where area steps in. This simple yet essential maths concept helps us navigate the world, making the abstract tangible.
What is area? Area in maths is about counting squares. When we define area, it means how many square units fit inside a shape or figure. If you picture a square 3O units long on each side, the area is 9 square units. This is because 9 squares, each 1 unit by 1 unit, can fit inside.
The concept of works the same way for all shapes, not just squares. From circles to triangles and more complex figures, the idea is to calculate how many square units fill up that shape.
This area definition helps us understand and describe the space around us!
Think about a farmer with a rectangular field. The length of his field is 200 feet, and the width is 100 feet. The farmer needs to know the total space of his field to buy the correct amount of seeds. He multiplies the length by the width and finds out his field is 20,000 square feet.
In a different scenario, consider an architect who is designing a room. She has a perfect square room, with each side being 12 feet. She calculates the area to ensure the furniture will fit and leave enough space to move around.
By multiplying the length and the width, she determines the room is 144 square feet. From farming to house design, the concept of area is essential.
Get 2 FREE weeks of Doodle!
Use code 2WKS_2026 to enjoy unlimited questions and games
Unlock unlimited maths questions
Put your learning into practice with fun exercises + games that are proven to boost ability!
Get 1 FREE month of Doodle!
Use code MONTH_2026 to enjoy unlimited questions and games
Have a go at some DoodleMaths questions
Select a year group
The formula to calculate area depends on the shape in question. For basic shapes such as a square or a rectangle, the area is the product of the length and the width.
However, their area formula becomes more complicated as the shapes become complex. Let’s take a look at a variety of area formulas by shape:
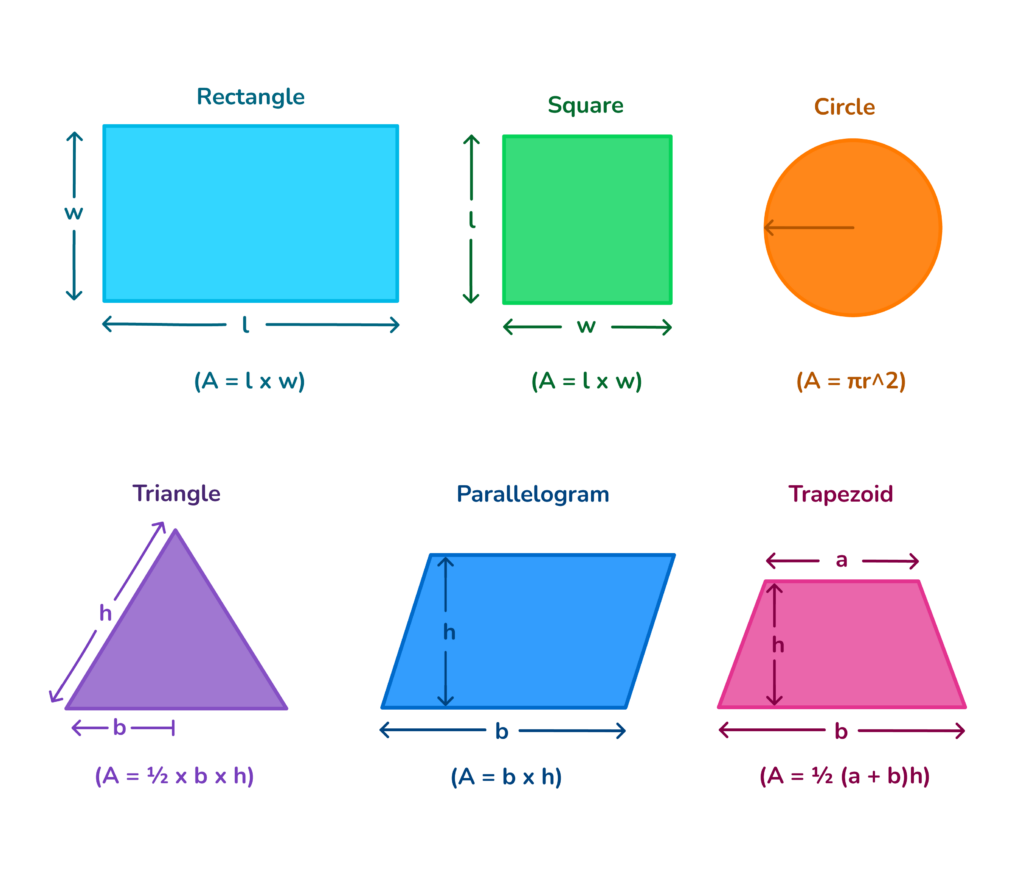
Here’s a quick table of all the area formulas for reference:
Shape | Area Formula |
Square/Rectangle | A = l x w |
Circle | A = πr^2 |
Triangle | A = ½ (b x h) |
Parallelogram | A = b x h |
Trapezium | A = ½ (a + b)h |
DoodleMaths is an award-winning app that’s filled with thousands of questions and games exploring multiplication, division and more!
Designed by teachers, it creates each child a unique work programme tailored to their needs, doubling their progression with just 10 minutes of use a day.* Try it for free!

*Based on earning 24 stars a day in DoodleMaths. Read full study
How to measure area relates to the surface covered by a shape, while the perimeter speaks to the total boundary length around that shape. Both play crucial roles in geometry, but they’re distinct. Think of a football field. The entire space where the game is played that’s the area. Now consider the distance you’d travel if you ran around the edge of the field. That’s the perimeter.
Volume measures the quantity of three-dimensional space an object inhabits. It’s like filling a box with small cubes and calculating how many fit inside. This measure considers not just the surface, as area does, but the entirety of the space within the object’s boundaries.
So while area and volume are related, they offer distinct ways to understand and interact with space. If you think of area as the carpet on your living room floor, volume would be the space your living room occupies, from floor to ceiling!
Click on the boxes below to see the answers!
The area of the rectangle is 40 square units.
The area of the circle is approximately 113.04 square units.
The area of the triangle is 6 square units.
The area of the trapezium is 49 square units.
The area of the square is 100 square units.
The area of the rectangle is 105 square units.
The area of the circle is approximately 78.5 square units.
The area of the triangle is 24 square units.
The area of the trapezium is 54 square units.
The area of the square is 144 square units.
The area is calculated to determine the size of a surface or a two-dimensional space. This is crucial in real-world situations, like buying sufficient paint for a room or determining the number of tiles required to cover a floor.
A practical example of area is when you need to paint a wall. You’d calculate the area of the wall to know how much paint you’ll need.
Area is just the inside space of a shape, counted in squares. Perimeter is the distance around the outside of the shape, counted in a straight line.

Understanding area is a crucial part of maths education. To further simplify the process, consider using resources like our app for maths help. It’s an effective tool to assist learners in understanding these fundamental concepts through interactive lessons and practice problems.

Parents, sign up for a DoodleMaths subscription and see your child become a maths wizard!
Lesson credits

Michelle Griczika
Michelle Griczika is a seasoned educator and experienced freelance writer. Her years teaching coupled with her double certification in early childhood education lend depth to her understanding of diverse learning stages. Michelle enjoys running in her free time and undertaking home projects.

Michelle Griczika
Michelle Griczika is a seasoned educator and experienced freelance writer. Her years teaching coupled with her double certification in early childhood education lend depth to her understanding of diverse learning stages. Michelle enjoys running in her free time and undertaking home projects.
Book a chat with our team
If you’d like to use Doodle’s browser version, please visit this page on a desktop.
To log in to Doodle on this device, you can do so through our apps. You can find out how to download them here: