Don’t be a square (at least not all the time). Learn all about rectangles.

Author
Taylor Hartley

Expert Reviewer
Jill Padfield
Published: July 2024


Don’t be a square (at least not all the time). Learn all about rectangles.

Author
Taylor Hartley

Expert Reviewer
Jill Padfield
Published: July 2024





Author
Taylor Hartley

Expert Reviewer
Jill Padfield
Published: July 2024


Key takeaways
We know our world is made up of all different shapes and sizes. One of the most common shapes out there is the rectangle! Rectangles share a lot of qualities with the square, but they’re not exactly alike.
Let’s learn all about rectangles: what they are, what sets them apart from their square siblings, and what to do when you’re trying to measure one!
Like a square, a rectangle is a two-dimensional (or flat) rectilinear shape with four sides and four right angles. By a rectangle’s definition, opposite sides must be equal and parallel to each other.
The two dimensions of a rectangle are length and width. Length is the longer side of a rectangle, while width is the shorter side of the rectangle.
Did you know? A square IS a rectangle. It has four sides, four right angles, and the opposite sides are equal and parallel. But, not all rectangles are squares because they might not have sides that are equal to each other.
Unlock unlimited maths questions
Put your skills to the test with fun exercises + maths games that are proven to boost ability!
Try DoodleMaths for free!
Select a year group
Take a look around you, and you will find rectangles everywhere! Need a few examples? Let’s take a look at some real-life rectangles.
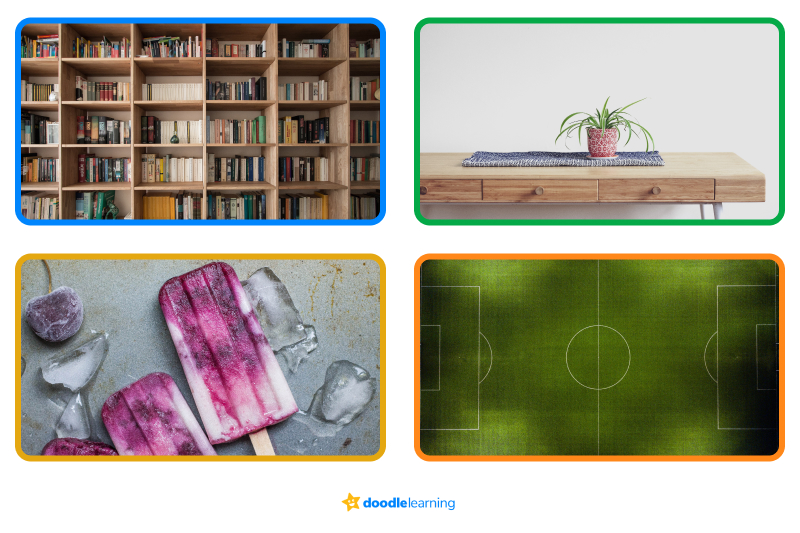

Rectangles have a few different names, which can be confusing if you don’t know what they mean. Let’s take a quick look at other names for rectangles so you can be in the know.
There are a few qualities a shape must have to be considered a rectangle. The shape must be a flat, 2D closed shape with:
Unlock unlimited maths questions
Put your skills to the test with fun exercises + maths games that are proven to boost ability!
DoodleMaths is an award-winning app that’s filled with thousands of questions and games exploring shape, multiplication and more!
Designed by teachers, it creates each child a unique work programme tailored to their needs, boosting their progression with 10 minutes of use a day. Try it free!

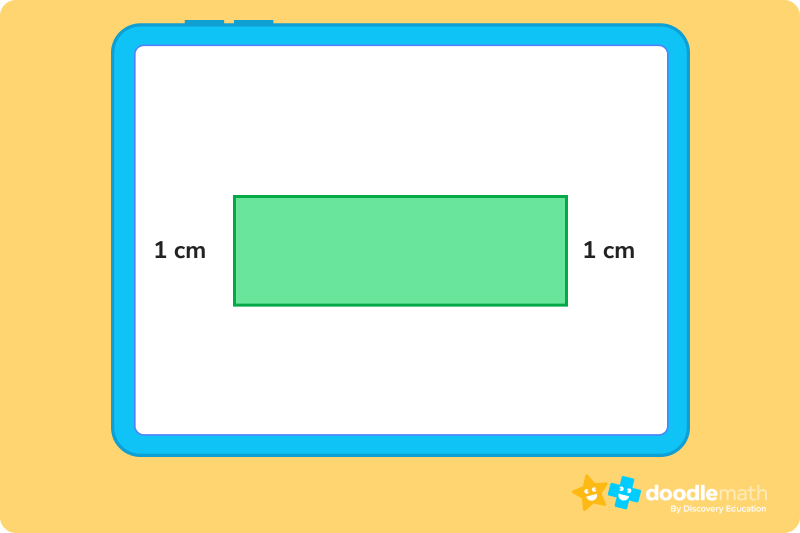
Like circles and squares, there are different parts to a rectangle. Understanding these parts will help you calculate the perimeter and area.
This is pretty simple: the length of a rectangle is how long a rectangle is. You can find the length by measuring one of the long sides of the rectangle. If one long side is not equal to the other long side, it is not a rectangle.

The width of a rectangle is how wide the rectangle is. You can find the width by measuring one of the two short sides of the rectangle. Like with length, if one of the short sides does not equal the other short side, it is not a rectangle.
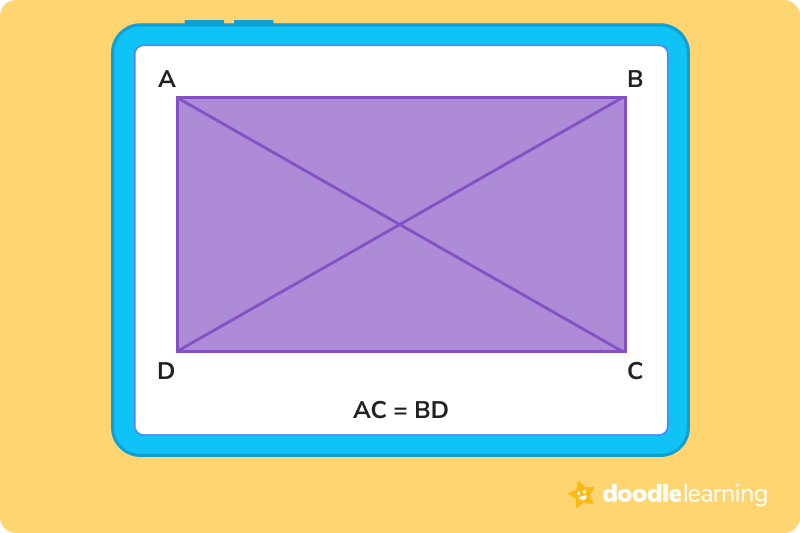
Diagonals are the line segments that connect the opposite corners of the rectangle. Diagonals should be equal to each other.
There’s plenty we can calculate using the parts of a rectangle. If we have the length and width, we can calculate the perimeter and the area. We can also use the length and width to calculate the length of the diagonal, but we will have to use an equation called the Pythagorean theorem.
Let’s go from easiest to hardest: measuring perimeter.
The perimeter is the measure of the outside of a rectangle. Put plainly, you can calculate the perimeter like this:
length + width + length + width = perimeter
Or, if you know how to multiply:
2(length) + 2(width) = perimeter
You can also write this as: (length + width) × 2 = perimeter
So, let’s find the perimeter of the rectangle we’ve been working with:
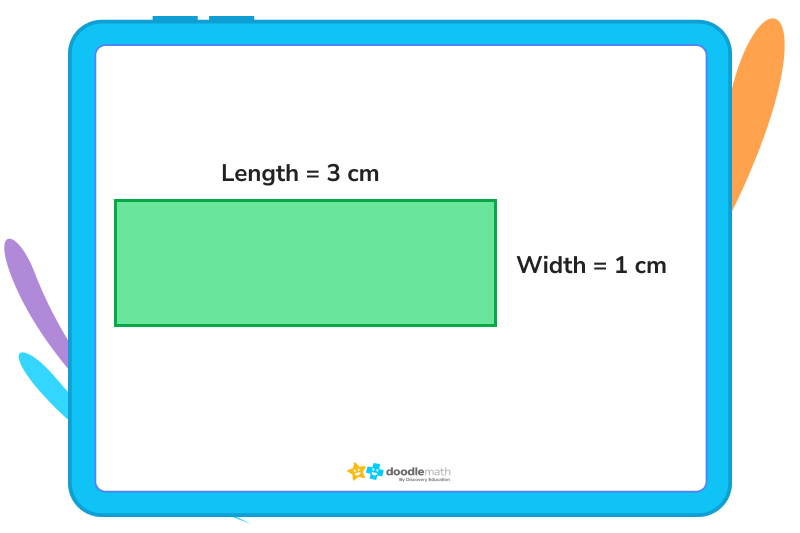
You can write this out either as
3 + 1 + 3 + 1 or
2(3) + 2(1) or
(3+1) × 2
Do your calculations, and you should find that the perimeter is 8 centimetres.
The area measures the inside of the rectangle or how much space it takes up. Calculating the area of a rectangle is pretty easy, as long as you can multiply!
Multiply the length by the width to find the area.
Put another way: length × width = area
Let’s find the area of our rectangle below:
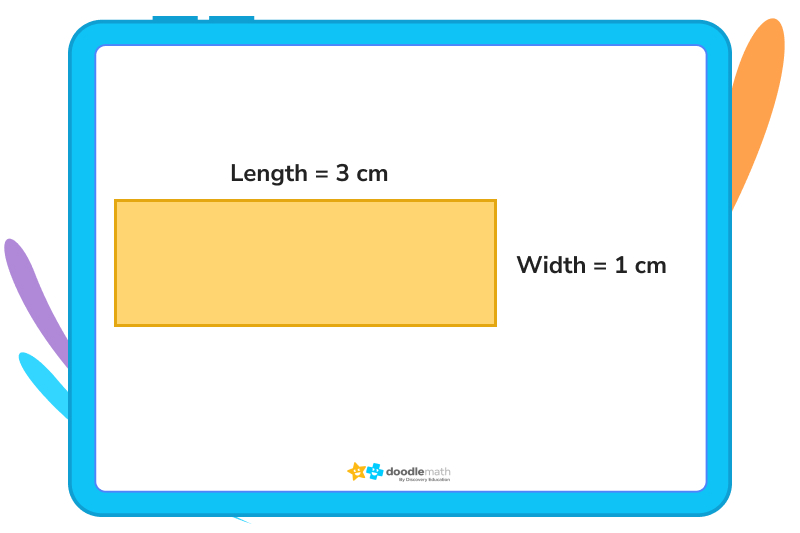
This means that the area is 3 × 1 = 3 centimetres.
Finding the length of diagonals using the length and width of the sides is a little more complicated. We have to use what’s known as the Pythagorean theorem, which you may not learn until 6th grade or later.
Let’s talk about how to do it, just in case you want to challenge yourself.
The diagonal of a rectangle is the hypotenuse, or the slanted side of a right triangle. It’s called a right triangle because it has a 90-degree angle at its base.
How do you calculate the hypotenuse of a right triangle?
The Pythagorean Theorem is as follows:
A2 + B2 = C2
A = length, B = width, and C = the length of the diagonal or the triangle’s hypotenuse.
The small 2 next to each letter means we need to square the number or multiply it by itself. So, using our example rectangle:
3 × 3 = 9
1 × 1 = 1
C = We don’t know, right?
So 9+1 = 10
10 = C2
So, to find C on its own, we take the square root of both sides, which is the opposite of squaring.
The diagonal is equal to the square root of 10, which can be written as √10.
If you know how to calculate decimals, this is equal to 3.162.
Now that we know what a rectangle is and how to find the perimeter and the area, let’s practise together! We’re going to walk through the next three practice problems with you.
1. Which of the following is a rectangle?
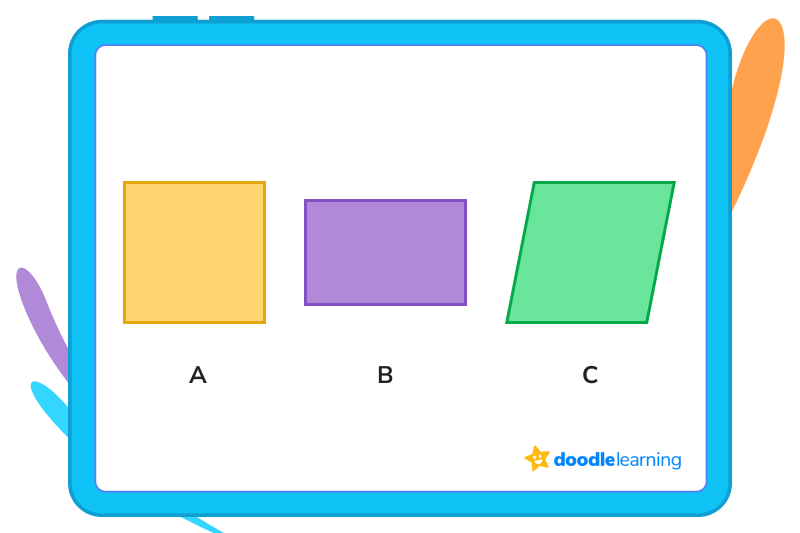
While all of these shapes are closed and two-dimensional, only D has equal, opposite sides that are parallel and four 90-degree angles, so D is the correct answer.
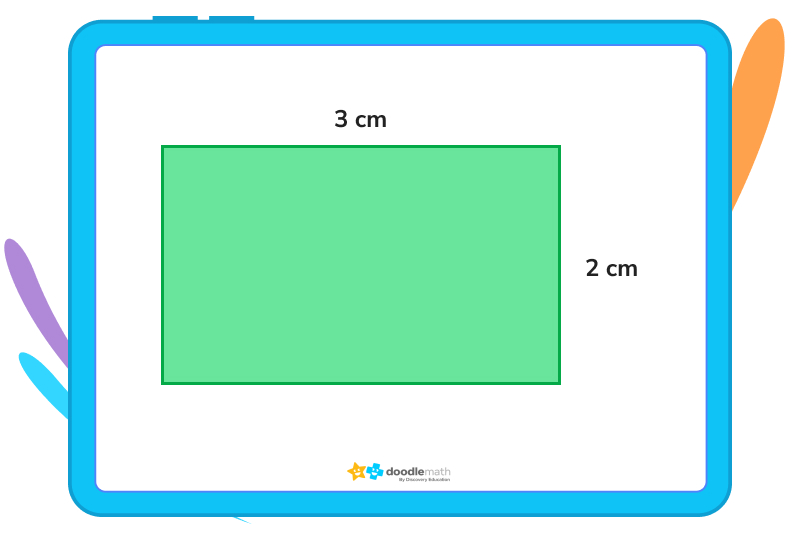
2. Using the rectangle above, calculate the perimeter.
So we know that if the top side of the rectangle is 3 centimetres, so is the bottom side. Additionally, since the right side of the rectangle is 2 centimetres, we know that the left side is also 2 centimetres.
That means the perimeter equals 3 + 2 + 3 + 2, or 2(3) + 2(2), or (3+2) × 2
If we add these sides together or multiply each side by 2, we’ll find out that the perimeter is 10 centimetres.
3. Using the rectangle above, calculate the area.
Remember, the area of a rectangle can be calculated by multiplying the length by the width. So:
3 × 2 = 6 centimetres
Ready to give it a go?
You’ve learned valuable skills about rectangles. Now it’s time to put your skills to the test! Take a look at these practice problems and find the right answer on your own.
Click to reveal the answer.
Both A and B are rectangles
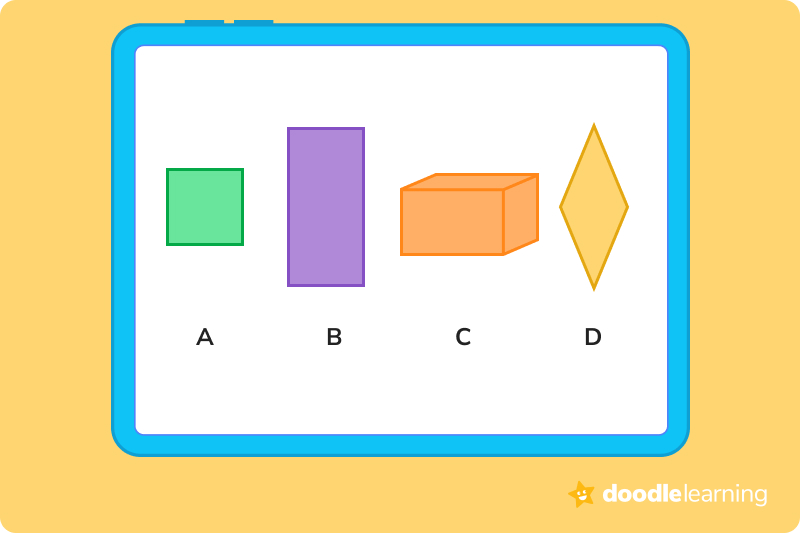
The answer is B, False.
The answer is A, Yes.
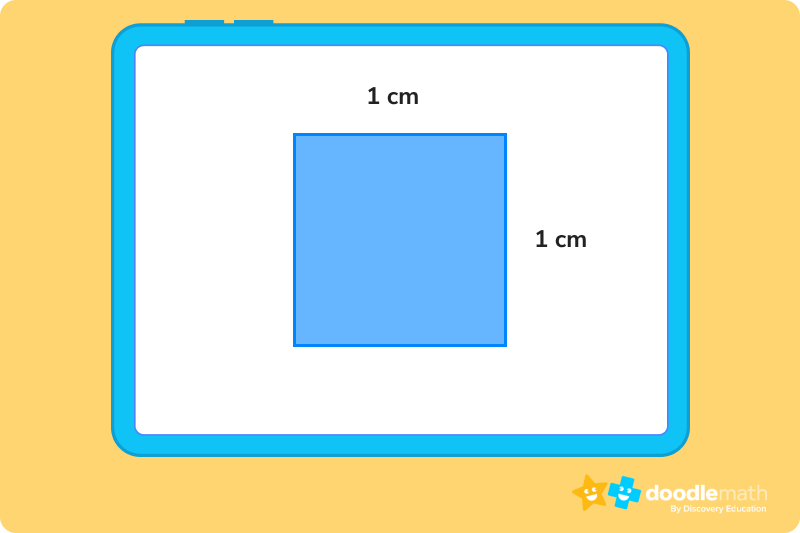
For the last two questions, use the figure below:
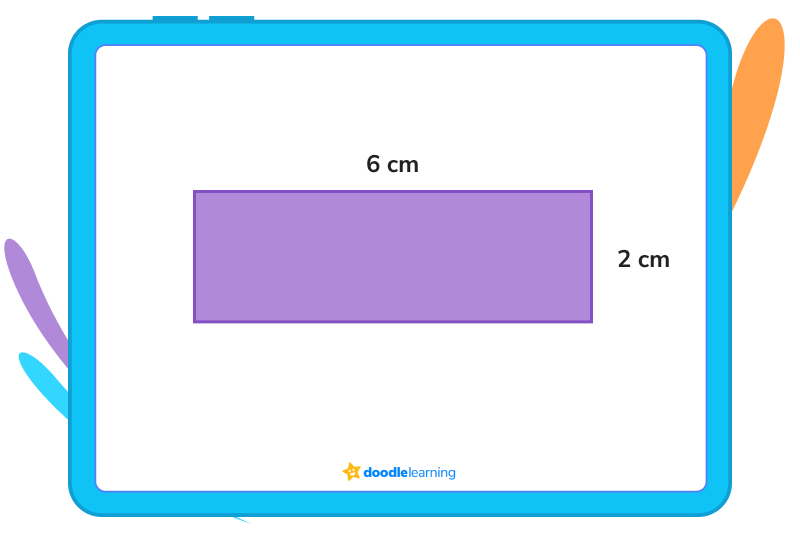
The answer is 16 cm
The answer is 12 cm
We understand that diving into new information can sometimes be overwhelming, and questions often arise. That’s why we’ve meticulously crafted these FAQs, based on real questions from students and parents. We’ve got you covered!
A rectangle must have 4 sides and 4 right angles. It has two pairs of parallel and opposite sides, too. The parallel and opposite sides must equal each other.
Other names for rectangles include equilateral quadrilateral and right-angled parallelogram.
To calculate the area of a rectangle, you simply measure its length by its width. So, if you have a rectangle with a length of 4 cm and a width of 2 cm, you multiply 4 by 2 to get 8 cm.
All squares are rectangles, but not all rectangles are squares! Because a square follows the properties of a rectangle, it must be considered a rectangle.
However, rectangles do not have to have 4 equal sides to be called rectangles.
To calculate the perimeter of a rectangle, you will add up all four of its sides.
So if you have a rectangle with a length of 5 cm and a width of 2 cm, you would add 5 + 5 + 2 + 2 (or multiply 5 by 2, since you have 2 sides that measure 5 cm, and 2 by 2 since you have 2 sides that measure 2 cm) to get 14 cm.


Parents, sign up for a DoodleMaths subscription and see your child become a maths wizard!
Both A and B are rectangles.
How did we get here?
The answer is B, False. A square is ALWAYS a rectangle, but a rectangle is not always a square.
The answer is A, yes. It is a square, and a square matches all qualities of a rectangle!
The answer is 16 cm.
How did we get here?
The answer is 12 cm.
How did we get here?
Lesson credits

Taylor Hartley
Taylor Hartley is an author and an English teacher. When she's not writing, you can find her on the rowing machine or lost in a good novel.

Jill Padfield
Jill Padfield has 7 years of experience teaching mathematics, ranging from Algebra to Calculus. She is currently working as a Business Analyst, working to improve services for Veterans while earning a masters degree in business administration.

Taylor Hartley
Taylor Hartley is an author and an English teacher. When she's not writing, you can find her on the rowing machine or lost in a good novel.

Jill Padfield
Jill Padfield has 7 years of experience teaching mathematics, ranging from Algebra to Calculus. She is currently working as a Business Analyst, working to improve services for Veterans while earning a masters degree in business administration.
Book a chat with our team
If you’d like to use Doodle’s browser version, please visit this page on a desktop.
To log in to Doodle on this device, you can do so through our apps. You can find out how to download them here: